



 )
)
|
manual abstract
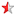
Notes 9. Jitter measured at crossing points and is the absolute value of the worst case deviation. 10. Measured at crossing points. 11. If input modulation is used; input modulation is allowed but not required. 12. The amount of allowed spreading for any non-triangular modulation is determined by the induced downstream tracking skew that cannot exceed the skew generated by the specified 0.6% triangular modulation. Typically, the amount of allowed non-triangular modulation is about 0.5%. 13. VOX is measured on external divider network. 14. VCOS = (clock output high voltage – clock output low voltage), measured on the external divider network. 15. VOL_ABS is measured at the clock output pins of the package. 16. IREF is equal to VISET/RRC. 17. Minimum IOL,ABS is measured at the clock output pin with RRC = 266 ohms or less. 18. ZOUT is defined at the output pins as (0.94V – 0.90V)/(I0.94 – I0.90) under conditions specified for IOL, ABS. Document Number: 001-42414 Rev. ** Page 8 of 13 [+] Feedback CY24272 AC Electrical Specification The AC Electrical specifications follow. [6] Parameter Description Min Typ Max Unit tCYCLE Clock Cycle time[19] 1.25 3.34 ns tJIT(cc) Jitter over 1-6 clock cycles at 400–635 MHz[20] – 25 40 ps Jitter over 1-6 clock cycles at 638–667 MHz – 25 30 ps L20 Phase noise SSB spectral purity L(f) at 20 MHz offset: 400–500 MHz (In addition, device must not exceed L(f) = 10log[1+(50x106/f)2.4] –138 for f = 1 MHz to 100 MHz except for the region near f = REFCLK/Q where Q is the value of the internal reference divider.) – –135 –128 dBC/Hz tJIT(hper,cc) Cycle-to-cycle duty cycle error at 400–635 MHz – 25 40 ps Cycle-to-cycle duty cycle error at 636–667 MHz – 25 30 ps .tSKEW Drift in tSKEW when ambient temperature varies between 0°C and 70°C and supply voltage varies between 2.375V and 2.625V.[21] – – 15 ps DC Long term average output duty cycle 45% 50 55% tCYCLE tEER,SCC PLL output phase error when tracking SSC –100 – 100 ps tCR,tCF Output rise and fall times at 400–667 MHz (measured at 20%–80% of output voltage) – 150 – ps tCR,CF Difference between output rise and fall times on the same pin of the single device (20%–80%) of 400–667 MHz[22] – – 100 ps Table 9. SMBus Timing Specification Parameter Description Min Max Units FSMB SMBus Operating Frequency 10 100 kHz TBUF Bus free time between Stop and Start Condition 4.7 .s THD:STA Hold time after (Repeated) Start Condition. After this period, the first clock is generated. 4.0 .s TSU:STA Repeated Start Condition setup time 4.7 .s TSU:STO Stop Condition setup time 4.0 .s THD:DAT Data Hold time 0 ns TSU:DAT Data Setup time 250 ns TTIMEOUT Detect clock low timeout Not supported TLOW Clock low period 4.7 .s THIGH Clock high period 4.0 50 .s TLOW:SEXT Cumulative clock low extend time (slave device) 25 ms CY24272 doesn’t extend TLOW:MEXT Cumulative clock low extend time (master device) 10 ms TF Clock/Data Fall Time 300 ns TR Clock/Data Rise Time 1000 ns TPOR Time in which a device must be operational after power on reset 500 ms Document Number: 001-42414 Rev. ** Page 9 of 13 [+] Feedback CY24272 Test and Measurement Setup Figure 3. Clock Outputs Swing Current Control Differential Driver CLK CLKB ISET RRC Measurement VTS Point VT R1 ZCH RT1 R2 R3CS RT2 Measurement VTS Point VT R1 ZCH RT1 R2 R3CS RT2 Example External Resistor Values and Termination Voltages for a 50. Channel Parameter Value Unit R1 33.0 . R2 18.0 . R3 17.0 . RT1 60.4 . RT2 301 . CS 2700 pF RRC 432 . VTS 2.5V V VT 1.2V V Signal Waveforms A physical signal that appears at the pins of a device is deemed valid or invalid depending on its voltage and timing relations with other signals. Input and output voltage waveforms are defined as shown in Figure 4 on page 11. Both rise and fall times are defined between the 20% and 80% points of the voltage swing, with the swing defined as VH–VL. Figure 5 on page 11 shows the definition of the output crossing point. The nominal crossing point between the complementary outputs is defined as the 50% point of the DC voltage levels. There are two crossing points defined: Vx+ at the rising edge of CLK and Vx– at the falling edge of CLK. For some waveforms, both Vx+ and Vx– are below Vx,nom (for example, if tCR is larger than tCF). Jitter This section defines the specifications that relate to timing uncertainty (or jitter) of the input and output waveforms. Figure 6 on page 11 shows the definition of cycle-to-cycle jitter with respect to the falling edge of the CLK signal. Cycle-to-cycle jitter is the difference between cycle times of adjacent cycles. Equal requirements apply rising edges of the CLK signal. Figure 7 on page 11 shows the definition of cycle-to-cycle duty cycle error (tDC,ERR). Cycle-to-cycle duty cycle is defined as the difference between tPW+ (high times) of adjacent differential clock cycles. Equal requirements apply to tPW-, low times of the differential click cycles. Notes 19. Max and min output clock cycle times are based on nominal outputs f...
Other models in this manual:Time Clocks - Rambus XDR CY24272 (216.6 kb)















